Boise State Service-Learning is at the forefront of integrating AI into planning and implementation.
What is AI Service-Learning?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Service-Learning is an educational approach that integrates artificial intelligence (AI) tools and methodologies with service-learning principles. This framework combines hands-on AI application with real-world community engagement, where students work on projects that apply AI to address specific community needs or issues. Through AI service-learning, students can deepen their understanding of AI tools and technologies while developing critical thinking, ethical reasoning, and social responsibility. Students can apply AI in a way that benefits local organizations, communities, and/or underserved populations. (Sass, 2024)
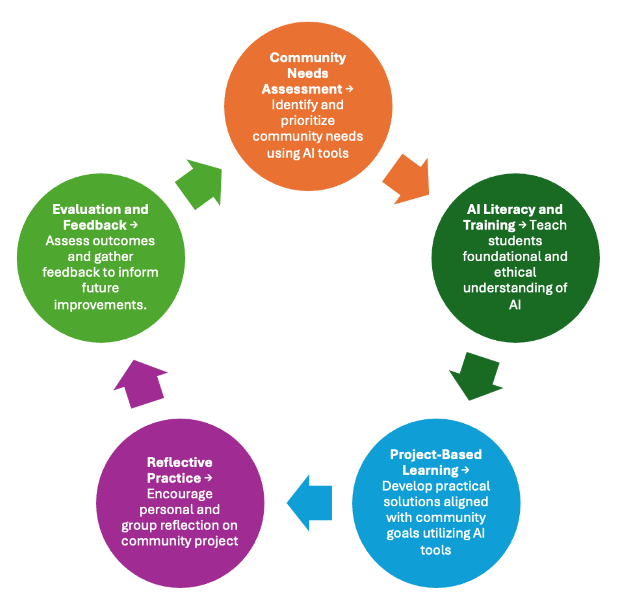
AI Service-learning is broken down into distinct phases that creates a process of collaboration, reflection and improvement. Here’s a step-by-step process that integrates these components:
Phase 1: Community Needs Analysis
- Establish Partnerships: Begin by identifying and connecting with community organizations, leaders, and stakeholders to understand their current challenges and needs. Generative AI can assist with this.
- Conduct Preliminary Research: Collect data about the community, including demographic, economic, and social information, to get a contextual understanding. Generative AI can assist with this.
- Document Findings: Summarize key findings, including specific needs and possible AI solutions, and share them with both community members. Confirm that these are the correct needs identified.
Phase 2: AI Literacy and Training
- Assess Baseline Knowledge: Conduct a brief survey or assessment to determine the AI knowledge levels of both students and community members.
- Develop Training Materials: Create accessible training resources, such as workshops, online tutorials, or in-person sessions, covering the basics of AI, data literacy, and the ethical implications of AI applications.
- Provide Hands-On Training: Organize interactive sessions where participants can explore AI tools, experiment with datasets, and understand basic concepts like machine learning, natural language processing, or data privacy.
- Evaluate Understanding: Assess participants’ learning through quizzes, reflections, or skill demonstrations, ensuring they’re ready to proceed to the project phase.
- Encourage Ongoing Learning: Offer optional advanced resources or learning modules for those interested in diving deeper, ensuring continuous engagement with AI topics.
Phase 3: Project-Based Learning
- Define Project Goals: Collaborate with community partners to define clear project objectives, focusing on tangible outcomes that address the needs identified in Phase 1.
- Develop a Project Plan: Outline project timelines, tasks, roles, and milestones. Ensure each team member understands their responsibilities and deliverables.
- Implement and Iterate: Begin work on the AI solution, encouraging teams to iterate based on feedback from stakeholders. Schedule regular check-ins to monitor progress, address challenges, and ensure alignment with community goals.
Phase 4: Reflective Practice
- Establish Reflection Points: Set up regular reflection sessions at key points in the project, such as after completing training, midway through the project, and at the end.
- Incorporate Ethical Reflections: Include prompts about ethical challenges, such as data privacy or bias, and ask participants to consider how they are addressing these issues within the project.
Phase 5: Evaluation and Feedback
- Define Evaluation Criteria: Establish specific metrics for assessing both student learning outcomes and community impact, such as AI tool usability, community satisfaction, and student skill development.
- Analyze Results: Review data collected from surveys, assessments, and project deliverables to evaluate the overall success of the project.
- Identify Areas for Improvement: Use the feedback to identify strengths and weaknesses in both the project design and the collaboration process. Focus on areas such as communication, technical skills, and community engagement.
- Share Findings and Celebrate Success: Present the findings to both students and community members, highlighting successes, challenges, and recommendations for future projects. This celebration fosters a sense of achievement and encourages ongoing collaboration.
- Plan Next Steps: Based on the evaluation, decide on potential follow-up projects, adjustments in training or project design, and any additional support that could strengthen future AI service-learning initiatives.
By following this process, you ensure a structured approach that emphasizes both learning and impact, while creating a sustainable model for integrating AI service-learning into community engagement projects.
Models for Community-AI Collaboration
- Participatory Design Model: Engage community members directly in the design and development of AI tools, ensuring that solutions meet actual needs and are user-friendly.
- Service Provider Model: Position AI tools as resources that serve existing community organizations by enhancing their capacity to deliver services.
- Capacity-Building Model: Educate community members on AI, enabling them to eventually maintain and even develop AI solutions independently.
- Consultative Model: Act as AI consultants, providing expertise to community partners while they retain control over decision-making and implementation