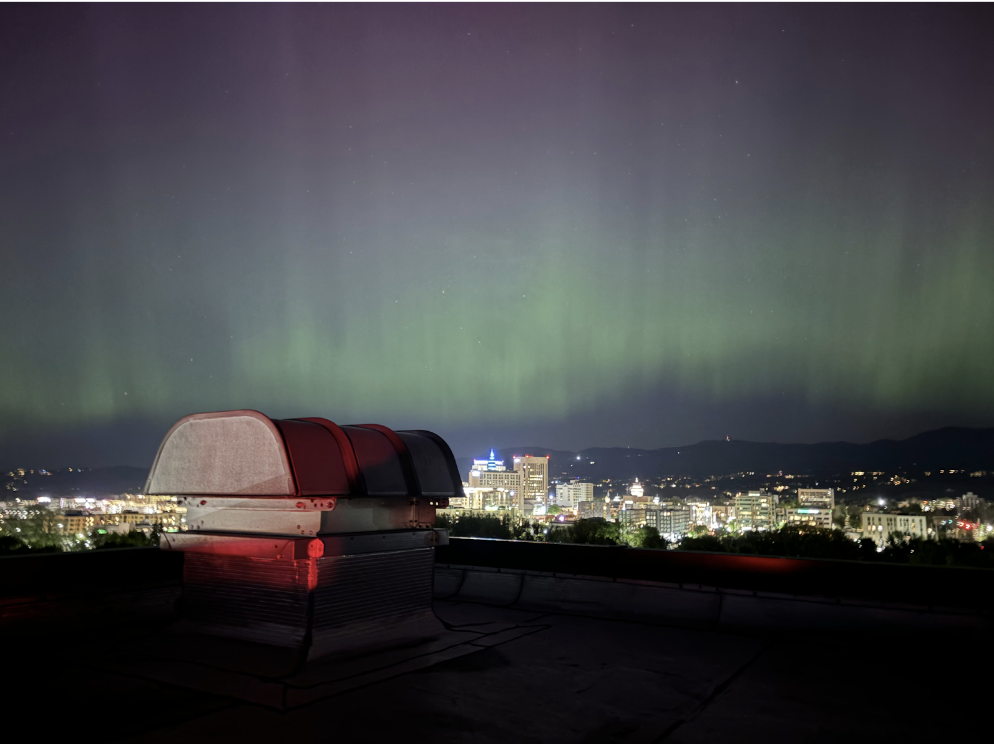

Earlier this May, people all around the world were given a dazzling show from the Northern Lights. Individuals in Idaho were no exception, where people as far down as Boise, Idaho could see the beautiful Aurora. While these lights were awe-inspiring, many might wonder: what exactly causes the Northern Lights and why could we see them so far down?
What causes the Northern Lights?
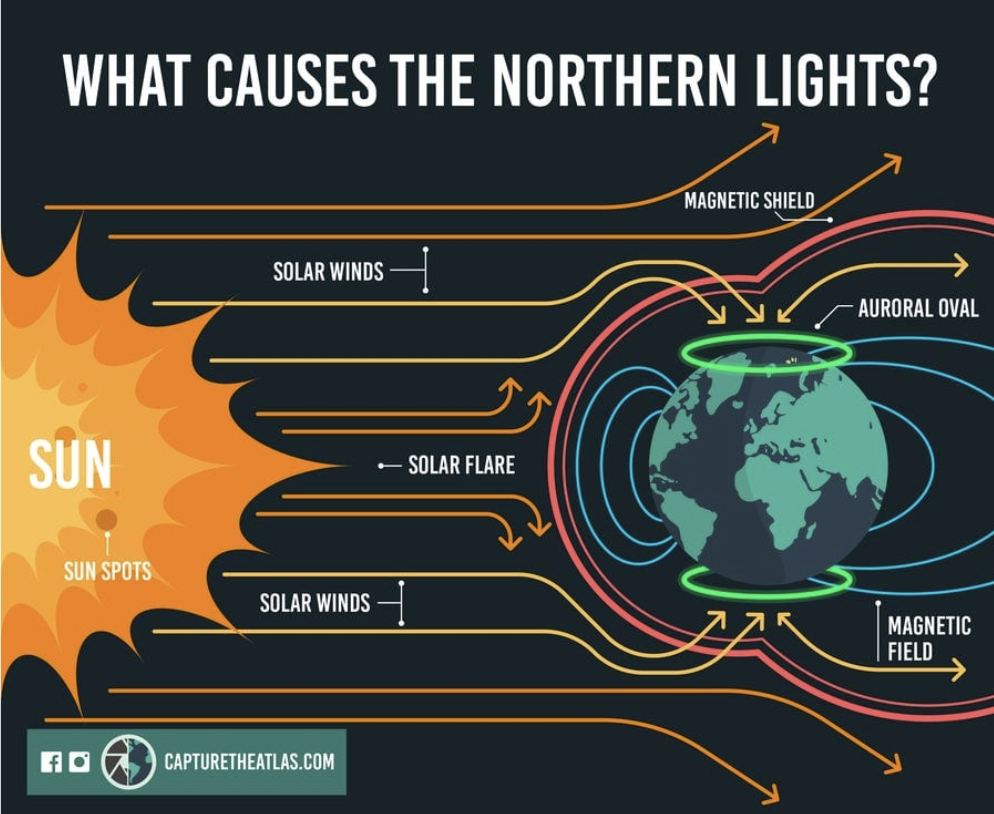
Northern lights occur due to strong activity from the Sun. Our Sun is extremely warm, with temperatures around 27 million degrees within its core. Due to this, the gas that makes up the Sun is so warm that the atoms within the gas cannot bind together and break apart into charged particles, creating something called plasma. This makes the Sun’s surface akin to a hot, charged particle soup. In addition, our Sun has a very strong magnetic field that likes to be active at times. Occasionally the strong magnetic fields on the Sun begin to twist and tangle.
However, just like a rubber band, when it tangles too much it snaps. This snap ends up releasing energy and shooting plasma out into space, which creates large solar flares.
When these “snaps” occur, these flares shoot out energized particles and solar winds throughout the entire Solar System. When these particles interact with Earth, however, two things can occur. In most cases, these particles will be repelled due to having the same net magnetic charge as our Earth’s magnetic field. However, occasionally these charged particles from the Sun will have an opposite charge and become attracted to our planet’s magnetosphere. When they are attracted, it greatly disturbs the magnetic field around our planet and creates a geomagnetic storm. During these storms, the energized particles enter into Earth’s atmosphere through the North and South Poles and mix with different gas molecules within our atmosphere, causing beautiful aurora to form.
Why could we see them so far down North?
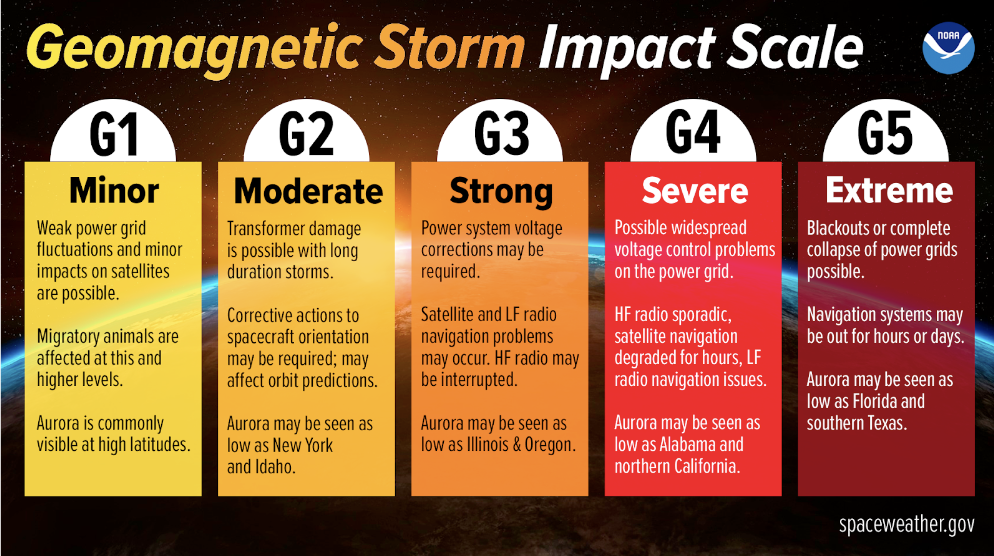
The reason we saw the Northern Lights so far down North is due to the intensity of the geomagnetic storm. The intensity of the storm is determined by how strong the changes within the Sun’s magnetic field are, very strong changes result in big sunspots and solar flares, which cause larger disturbances here on Earth. These storms are rated on a scale of G1 to G5 in severity, with G1 having minor effects and G5 having extreme effects on the Earth. The Northern lights that just visited us were caused due to a G5 geomagnetic storm, the first since 2003, and caused lights to be seen as far down as Alabama.
Why does the intensity change?
The intensity of geomagnetic storms changes due to an 11-year cycle of solar activity within the Sun. During these 11 years, the Sun’s magnetic field flips so that North becomes South and South becomes North. This cycle is characterized by two stages, Solar Minimum and Solar Maximum. Solar minimum is when the Sun isn’t as active, resulting in fewer sunspots, solar flares, and less severe geomagnetic storms. However, solar maximum is when solar activity increases significantly and creates more intense and frequent geomagnetic disturbances.
Will we see them again?
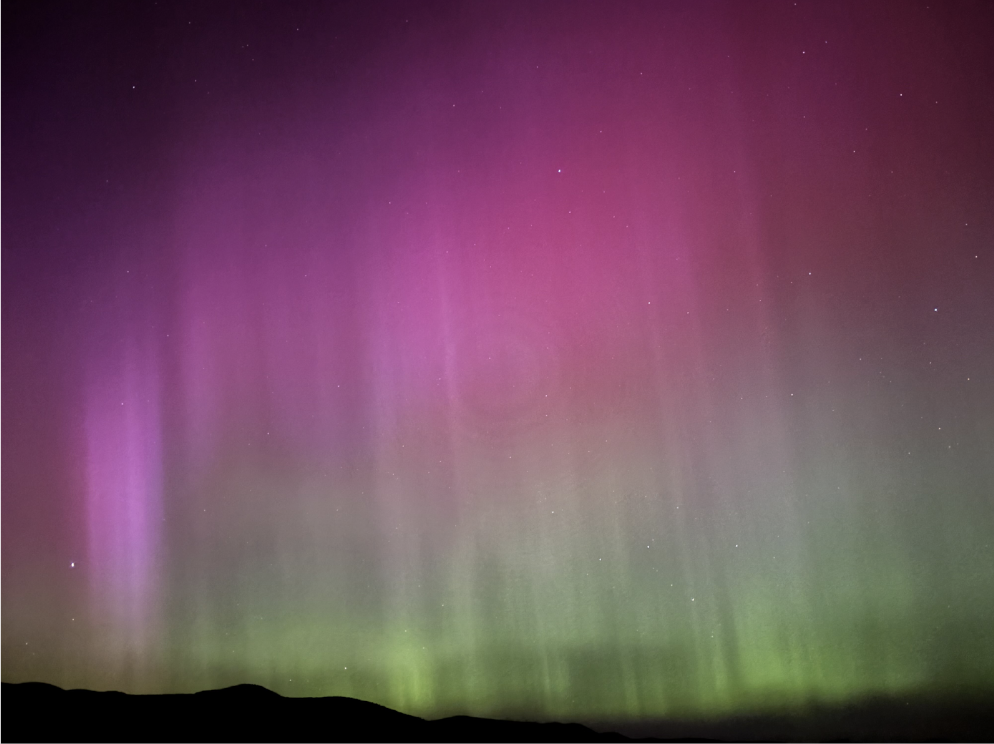

This year our Sun has just entered the solar maximum stage of its 11-year-long cycle. This will cause our sun to be much more active for around the next decade, resulting in more intense geomagnetic storms hitting our planet and in return more Aurora. So don’t lose hope if you were unable to see the northern lights this May, we will likely be able to see them once again in the near future!
Article written by Chandler Beasley, 2024 AstroTAC member.