In a previous article, we explored the current situation of greenhouse gas emissions across the United States. This week, we delve deeper into the state of Idaho, examining the primary contributors to these emissions and the potential implications for the Gem State’s environment and future.
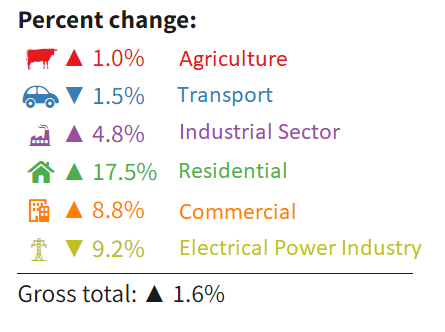
The following picture from Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) shows that Idaho’s Green House Gas (GHG) emissions in 2022 increased by 1.6% compared to 2021.
Now, let’s have a look at the below pie chart to understand the major contributors of GHG in Idaho by economic sector, 2022.
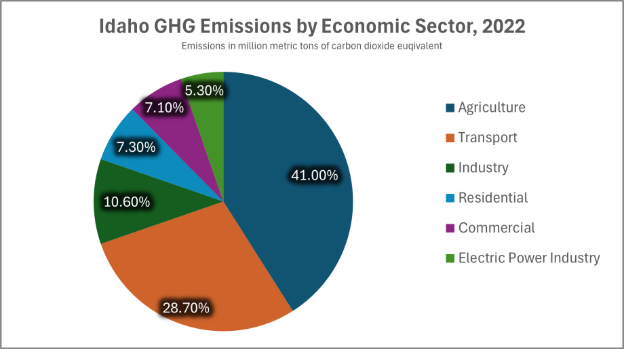
According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), agriculture is the most significant source of greenhouse gas emissions in Idaho, accounting for approximately 41% (15.774 MMT CO2 eq) of the state’s total emissions in 2022. Also, GHG emissions in the agriculture sector increased by 1% compared to 2021. This is primarily due to the huge contribution of Idaho to the national livestock and agriculture industry. The process of raising these animals releases methane, a potent greenhouse gas, through their digestive systems and manure. Additionally, the cultivation of crops such as potatoes, hay, wheat, and sugar beets contributes to emissions through the use of fertilizers, water, machinery, and other agricultural inputs.
Transportation: A Second Contributor
The transportation sector is the second-largest contributor to greenhouse gas emissions in Idaho, representing around 29% of the state’s total emissions. This is primarily driven by the increasing number of vehicles on the road, as well as the reliance on fossil fuels such as gasoline and diesel. The growth of urban areas and the expansion of transportation infrastructure have further added to this issue. According to statista.com, Idaho is among the states that gained the population growth of 1.1% to 1.5% from 2022 to 2023*.
Moreover, Idaho is among the states with lower adoption rates for electric vehicles (EVs). According to U.S. Department of Energy‘s latest data for September 2024, Idaho has just 8,501 registered EVs. In comparison, California ranks first with 1,256,646 EVs, and Florida second with 254,878 EVs in the state.
Other Notable Sources:
While agriculture and transportation are the primary drivers of greenhouse gas emissions in Idaho, other sectors also contribute to the problem. These include:
- Industrial Processes: Emissions from manufacturing facilities, such as those involved in food processing, chemical production, and technology development contributed around 10.6% to Idaho’s GHG emissions.
- Commercial and Residential Sector: The burning of fossil fuels for lighting, cooling and heating homes, businesses, and institutions contributed 14.4% to Idaho’s GHG emissions.
- Electrical Power Generation: According to Idaho Power, Idaho has significant green electricity resources with 54.3% of energy being generated from green sources like hydropower, solar, windmills, and geothermal sources. There is still a huge improvement gap available as this sector contributed 5.3% to Idaho’s GHG emissions in 2022.
The Road Ahead:
Addressing the issue of greenhouse gas emissions in Idaho will require a multifaceted approach involving individual industrial actions and policy changes. Some potential strategies include:
- Support Sustainable Agriculture: By adopting sustainable farming practices that reduce emissions, such as utilizing green energy sources, implementing water-saving techniques, considering electric machinery, and utilizing cover cropping and rotational grazing, we can significantly mitigate agriculture’s environmental impact in Idaho.
- Invest in Public Transportation: Idaho’s public transportation system is very limited. Expanding public transportation options can reduce the number of vehicles on the road and lower transportation emissions.
- Promote Electric Vehicles: Encouraging electric vehicles can help reduce emissions from the transportation sector. Also, developing the EVs friendly infrastructure i.e. installation of charging stations will attract the population towards the use of EVs.
- Transition to Renewable Energy: Increasing the use of renewable energy sources such as solar and hydropower can reduce the dependency on fossil fuels and lower emissions.
- Improve Energy Efficiency: Implementing energy-efficient practices in homes, businesses, and industries can help reduce energy consumption and associated emissions.
By taking a comprehensive approach to addressing greenhouse gas emissions, Idaho can work towards a more sustainable future and protect its environment for generations to come.
In the coming articles, we will cover the major sources of GHG emissions in Boise and then will discuss the major GHG contributors like Agriculture, Transport, and Electrical Power in detail. Have any questions or want to know more about GHG emissions in Idaho? Let us know at COBEEthics@boisestate.edu!
Sources
This article utilized data from the following sources: