Sustainable supply chain and circular economy are transforming how businesses operate. The traditional linear supply chain follows a “take-make-dispose” model, which leads to excessive waste and resource depletion. A sustainable supply chain and circular economy aim to minimize environmental impact, maximize resource efficiency, and create long-term economic benefits.
Understanding the Linear Supply Chain Model:
A linear supply chain follows a straightforward path: raw materials are extracted, processed into products, distributed, consumed, and then discarded as waste.
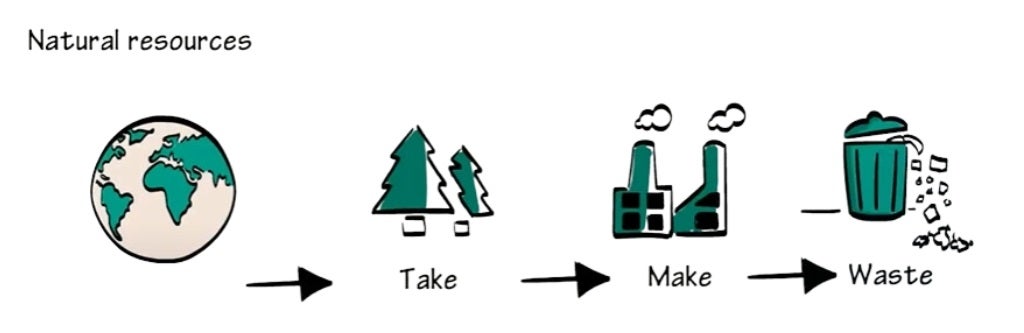
This model dominates many industries but is proving to be unsustainable due to resource depletion, environmental degradation, and increased costs. Due to rising commodity prices and waste management challenges, the need for sustainable supply chain models has increased.
What is a Sustainable Supply Chain?
A sustainable supply chain integrates environmental, social, and economic considerations into each stage. It ensures that sourcing, manufacturing, distribution, and disposal processes minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency. Companies that adopt sustainable supply chains focus on reducing carbon footprints, and ethical sourcing. It also optimizes logistics to lower emissions and waste.
Key characteristics of a sustainable supply chain include:
- Eco-friendly Sourcing: Using renewable, recyclable, and biodegradable materials.
- Energy Efficiency: Implementing energy-saving production and transportation methods.
- Ethical Labor Practices: Ensuring fair wages, union rights, and safe working conditions.
- Waste Reduction: Implementing recycling and upcycling initiatives to minimize landfill waste.
The Shift to a Circular Economy:
A circular economy is an alternative to the linear model. It is designed to eliminate waste and keep materials in use for as long as possible. Before diving into how circular economy helps achieve a sustainable supply chain, let’s first understand what circular economy is.
Understanding Circular Economy:
The circular economy is a transformative model that diverges from the traditional linear “take-make-dispose” approach. It focuses on creating a regenerative system that minimizes waste, optimizes resource use, and creates long-term sustainability. In contrast to the linear model, which relies on the extraction of raw materials and discards them after use, the circular economy is designed to keep products, materials, and resources in use for as long as possible. See the below picture to understand how the circular economy works.
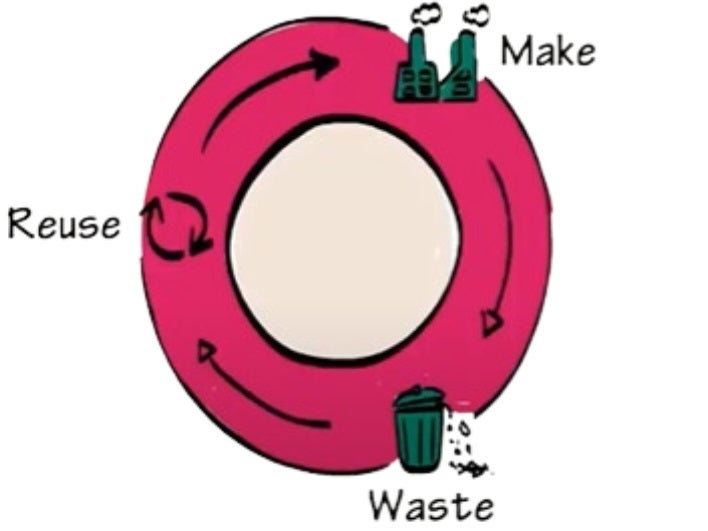
Products are designed for durability, repairability, and recyclability. This reduces the need for raw materials extraction and minimizes the environmental impact.
This system emphasizes two key material flows: biological materials, which return to the natural environment to regenerate natural capital, and technical materials, which remain within the production and use cycles without losing their quality.
The circular economy also promotes the sharing economy. Through this, consumers can access goods and services without the need for ownership. This further enhances the efficient use of resources. Other than environmental benefits, a circular economy also generates new business opportunities and revenue streams. It enables companies to rethink traditional value creation and find opportunity gaps to boost their businesses.
How Circular Economy Benefits the Sustainable Supply Chain:
The adoption of a circular economy offers several advantages for supply chains. It enhances efficiency, sustainability, and resilience. Here are the key benefits:
- Cost Savings: By reusing materials, recycling products, and reducing waste, companies can significantly lower production costs. Circular practices, such as remanufacturing or extending product life, help businesses save money on raw materials and reduce the need for expensive extraction of resources.
- Increased Resilience: A circular economy reduces reliance on finite resources, which are further subject to fluctuations in supply and price. By creating closed-loop systems and recycling materials, businesses can mitigate the impact of market disruptions and commodity price volatility. This enables companies to build more resilient supply chains that are less vulnerable to global supply shocks.
- Regulatory Compliance: Governments worldwide are continuously implementing strict environmental policies. By adopting circular economy practices, businesses can ensure compliance with these regulations. They can also avoid potential fines and enhance their environmental credentials.
- Innovation and New Business Models: The circular economy encourages the development of innovative business models. This includes product-as-a-service, sharing platforms, and recovery and recycling initiatives. These models not only reduce waste but also create new revenue streams.
- Positive Environmental Impact: The shift to a circular economy contributes to environmental sustainability by reducing carbon emissions, minimizing waste, and promoting the use of renewable resources. Companies that adopt circular practices help lower their ecological footprint and contribute to global efforts to combat climate change.
Conclusion
Transitioning to a sustainable supply chain and circular economy is no longer an option but a necessity. As businesses and governments recognize the importance of sustainability, adopting circular practices will drive long-term success, economic resilience, and environmental preservation. Companies that embrace these principles will not only reduce their ecological footprint but also gain a competitive edge in the evolving global market.
In upcoming articles, we will explore circular economy and sustainable supply chain practices across different industries. We will also examine their adoption, claims, and past challenges.
Have any questions or want to know more about Sustainable Supply Chain & Circular Economy? Please reach out to the COBE Ethics Chair at COBEEthics@boisestate.edu. Explore the College of Business and Economics (COBE) website to learn more about undergraduate and graduate degree programs in supply chain management.